Toxoplasmosis:
• Caused by protozoan – Toxoplasma gondii
• The domestic cat is the definitive host with infections via:
• Ingestion of cysts (meats, garden products)
• Contact with oocysts in faeces
• Much higher prevalence of infection in European countries (ie France, Greece)
• Acute infection usually asymptomatic
• 1/3 risk of fetal infection with primary maternal infection in pregnancy
• Infection rate higher with infection in the 3rd trimester
Clinical Manifestations
• Most (70-90%) are asymptomatic at birth
• The classic triad of symptoms:
• Chorioretinitis
• Hydrocephalus
• Intracranial calcifications
• Other symptoms include fever, rash, HSM, microcephaly, seizures, jaundice, thrombocytopenia, lymphadenopathy
• Initially asymptomatic infants are still at high risk of developing abnormalities, especially chorioretinitis
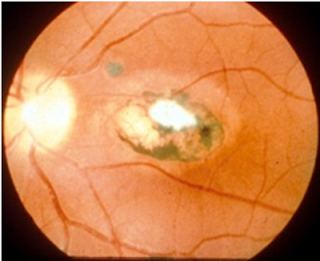 |
| Chorioretinitis |
Diagnosis:
• Maternal IgG testing indicates past infection (but when…?)
• Can be isolated in culture from the placenta, umbilical cord, infant serum
• PCR testing on WBC, CSF, placenta
• Not standardized
• Newborn serologies with IgM/IgA
Toxo Screening:
• Prenatal testing with varied sensitivity not useful for screening
• Neonatal screening with IgM testing implemented in some areas
• Identifies infected asymptomatic infants who may benefit from therapy
Prevention and Treatment:
• Treatment for pregnant mothers diagnosed with acute toxoplasmosis.
• Spiramycin daily
• Macrolide antibiotic
• Small studies have shown this reduces the likelihood of congenital transmission (up to 50%)
• If infant diagnosed prenatally, treat mom
• Spiramycin, pyrimethamine (anti-malarial, dihydrofolate reductase inhibitor), and sulfadiazine (sulfa antibiotic)
• Leucovorin rescue with pyrimethamine
• Symptomatic infants
• Pyrimethamine (with leucovorin rescue) and sulfadiazine
• Treatment for 12 months of total
Improved neurologic and developmental outcomes demonstrated (compared to untreated pts or those treated for only one month
Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post