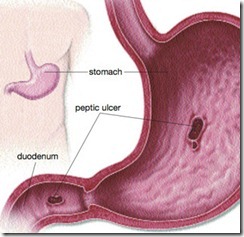
 Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD): definition
Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD): definition
A circumscribed ulceration of the gastrointestinal mucosa occurring in areas exposed to acid and pepsin and most often caused by Helicobacter pylori infection.MORE THAN 5 mm in diameter.
• MAYBE ACUTE OR CHRONIC.
EROSION and Ulcer
• A BREAK IN THE GI MUCOSA LESS THAN 5 mm IN DIAMETER - NOT PENETRATING MUSCULARIS MUCOSA IS CALLED EROSION. Deeper erosions are called ulcers.•EROSION MAY OCCUR IN ACID SECRETING AND NON- ACID SECRETING MUCOSA
• PERISTALSIS NOT AFFECTED IN EROSION
• EROSION HEALS RAPIDLY.
Sites of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
• PUD may occur in any area where acid and pepsin are present• Commonest sites:
– Duodenum especially first part “duodenal bulb”– Stomach especially over the lesser curve
• Other sites:
– The lower end of the oesophagus– site of gastrojejunal anastomosis
– Opposite to Meckel’s diverticulum
AETIOLOGY OF Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
• HELICOBACTER PYLORI- ASSOCIATED ULCERS• NSAID-RELATED ULCERS.
• HYPER ACID SECRETORY STATES, For example, Z-E SYNDROME, IDIOPATHIC.
Pathogenesis of Peptic Ulcer Disease (PUD)
• IMBALANCE BETWEEN AGGRESSIVE AND DEFENSIVE FACTORSProtective factors
- saliva, food, duodenal fluid, mucus - mucine, fast regeneration capability of gastric epithelial cells, well perfused gastric mucosa
AGGRESSIVE FACTORS
• ACID AND PEPSIN
- bile acids (reflux), Helicobacter pylori, drugs (analgesics, aspirin, ), nicotine, alcohol
MECHANISMS OF ACID SECRETION
• NERVOUS• ENDOCRINOLOGICAL
– Gastrin
• PARACRINOLOGICAL
– GRP: increase secretion of acid
– Somatostatin: decreases secretion of acid
– Histamine: stimulates secretion of acid
Diagnosis of PUD
• The clinical picture is suggestive but not diagnostic• Diagnosis best by endoscopy
• Barium meal less helpful
• no role for serum gastrin or gastric acid studies in usual ulcers, it is indicated if ZE syndrome is suspected
• Evaluation for H pylori infection
• The gastric ulcer should be biopsied to exclude malignancy
Diagnosis of Helicobacter pylori infection
• Invasive( through endoscopy)
– Gastric biopsy and staining– culture of Bx specimen
– Tests using urease enzyme in Bx specimens
• Non-invasive:
– Urea breath test– H.pylori antibodies
– Stool antigen
– Salivary antigen
Complications of PUD
Ø Bleeding – Chronic bleeding causes anemia and it is minor and usually remain unnoticed. Acute bleeding may lead to hematemesis.Ø Perforation – usually occurs in anterior gastric wall causes
- acute violent pain
- bleeding can be present
Ø Penetration - of the ulcer deeply through the whole wall into
neighbour organ (pancreas, liver)
Ø Stenosis - narrow of the lumen caused by scar, oedema or
inflammatory infiltration after healing of the ulcer
- rise only at pyloric localization
- vomiting of a huge volume of gastric content
TREATMENT OF PEPTIC ULCER DISEASE
• AIM OF TREATMENT:
– RELIEVE SYMPTOMS– HEAL THE ULCER
– PREVENT COMPLICATIONS
– PREVENT RECURRENCES
Lifestyle modification in PUD
– REST– RELAXATION
– GOOD SLEEP
– DIET:
• Take a bland diet
• Take frequent small meals
• Avoid caffeine-containing beverages
• Avoid too many spices
• Take fibre
• vitamin E and dietary fatty acids
HISTAMINE- RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (H2-Blockers )
• CIMETIDINE 400mg b.d or 800mg at bed time
• RANITIDINE 150mg b.d. or 300mg at bed time
• FAMOTIDINE 20mg b.d. or 40mg at bed time
• NIZATIDINE 150mg b.d. or 300mg at bed time
HISTAMINE- RECEPTOR ANTAGONISTS (H2-Blockers )
• Act through blocking H2 receptors in the parietal cells
• Suppress nocturnal acid secretion by more than 90%
• Suppress 24-hour acid secretion by 50-70%
• Side effects :
– CNS effects: headache, mental confusion– Reversible gynecomastia and impotence.
– Interaction with drugs metabolized through hepatic cytochrome P-450 microsomal enzymes
ANTACIDS
• Rapid symptomatic relief• Cheap
• Large amounts are required to heal ulcers leading to undesirable side effects.
• If taken on an empty stomach; they are effective only for 10-20 minutes
• If taken one hour after meals they are effective for 2-3 hours.
• Tablet preparations are less effective than suspensions
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS(PPIs)
• Suppress acid secretion by non-competitively and irreversibly inhibiting the H+ , K+- ATPase of the gastric parietal cells• Inhibit over 90%of 24-hour acid secretion
• Heal 50% of DUs by 2 weeks, 90% in 4 weeks and almost all by 6-8 weeks
PROTON PUMP INHIBITORS(PPIs)
• Omeprazole: 20,40 mg
• lansoprazole: 15, 30 mg
• pantoprazole: 20, 40 mg
• rabeprazole: 10, 20 mg
• esomeprazole:20, 40 mg
• Tenatoprazole: 40 mg: longer duration of action
New Therapies
• Potassium-competitive acid blockers: P-CAB: Block secretion of acid by blocking the exchange of K+ by H+: still investigational AZD0865
Eradication therapy for H.Pylori
• In vitro Helicobacter pylori highly sensitive to many antibiotics• In vivo, Helicobacter pylori sensitive to the following agents:
– amoxicillin
– tetracycline
– clarithromycin
– Metronidazole, tinidazole
– bismuth
– PPIs
– Second line drugs: Levofloxacin, gatifloxacin, rifabutin
Eradication therapy for H.Pylori
• Use a triple or quadruple regimen for 7-14 days.
• Efficacy of the regimen depends upon drugs used, compliance of the patient, resistance pattern of HP in the area
• Relapse rate drops to less than 10% per year after successful eradication
SUCRALFATE
• 1gm 4 times daily on an empty stomach• Healing rate: 70-80% within 8 weeks
• binds with the proteinaceous base of the ulcer
• increasing local mucosal production of PGs
• Side effects:
– constipation– nausea
– reduces the absorption of some drugs
– binds phosphate in the gut
PROSTAGLANDINS
• Inhibit gastric acid secretion and has cytoprotective effects• They are less effective than H2- blockers
• side effects:
– abdominal cramps– diarrhea
– not cost-effective
• Indicated for prophylactic use rather than for treatment
Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post