Type One Hypersensitivity Reaction-Causes-Types-Phases-Mediators and Examples Of Type One Hypersensitivity Reaction
Type One Hypersensitivity Reaction-Causes-Types-Phases-Mediators and Examples Of Type One Hypersensitivity Reaction
Type I Hypersensitivity Reaction:
•A rapidly developing immunologic reaction occurring within minutes after the combination of an antigen (allergen in this case) with antibody bound to mast cells in individuals previously sensitized to that antigen. These reactions are often called allergies.Key:
Ig= Immunoglobulin , Abs = Antibodies, Ags= Antigens, IgE = Immunoglobulin E,
Pathogenesis Of Type One Hypersensitivity Reaction
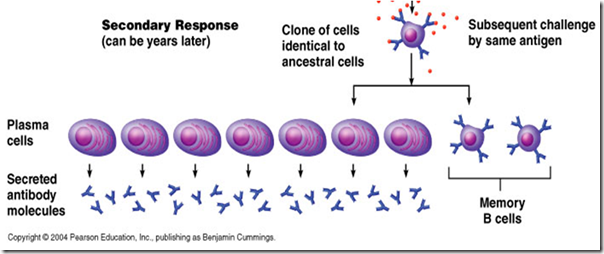
•Primary response (Sensitization of the person):

–Antigens (Allergens) bind to B lymphocytes & stimulate them. They form both plasma cells and memory cells. The plasma cells produce IgEs (attach to mast cells in the vicinity) while the memory cells remain as armed guards in that area. This primary response is usually weak and subsides by itself if the dose of the Ags is small or the exposure is single and for a short time but the Memory B cells remain for years.
Secondary response (exposure of a sensitized person to the same antigen)
•Memory B cells start response to the same antigen (Allergen) on 2nd exposure very strongly and secrete numerous IgEs which besides binding with Ags are also attached to IgE-Fc receptors on mast cells (present around the vessels, nerves and subepithelial areas). The allergen reacts with more than one Abs on the surface of mast cells. In this way, cross-reaction of Abs and Fc receptors on mast cells occurs. This cross-reactivity stimulates mast cells to secrete their preformed contents (histamine, proteases, heparin, leukotrienes and prostaglandins.) and to synthesize new ones which are the mediators of the type1 hypersensitivity reaction.
PHASES of Type I (IMMEDIATE) HYPERSENSITIVITY
There are Two phases of type 1 hypersensitivity reactions – Immediate and Late Phase
•Immediate phase occurs in minutes due to the release of mast cell contents (mast cell degranulation) causing vasodilatation, vascular leakage, smooth muscle spasm and can lead to anaphylaxis, shock, oedema, dyspnea and death.
• Late phase occurs in hours to days. It is due to the recruitment of inflammatory cells like Eosinophils, PMNs, T- Cells towards the site causing damage to various tissues.
Examples of type I hypersensitivity reaction
•Allergic rhinitis, bronchial asthma(Asthma-Causes-Pathogenesis-Clinical Signs Article), allergic gastroenteritis, allergic conjunctivitis, skin allergy, systemic anaphylaxis and local immediate hypersensitivity reactions like urticaria etc.
Comments
Post a Comment
Post Your Reply and Give Your Opinion About the Post