Celiac disease is a disease of the digestive system.
what is affected by the celiac disease?
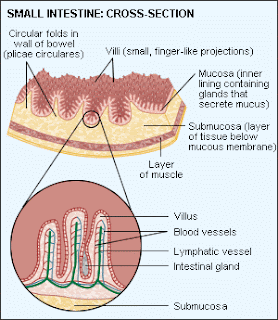
our intestine has villi. villi are finger-like projections in the inner surface of the small intestine. Villi have further microscopic finger-like projections called microvilli. These villi and microvilli greatly increase the surface area of the small intestine and these are responsible for absorption of nutrients.
In celiac disease, these villi are affected and get damaged. and the person shows the sign and symptoms of diarrhoea abdominal pain etc (explained later)
Why These Villi are affected?
Celiac disease is a disease of malabsorption ( nutrients are not absorbed properly ) and autoimmune response to gluten.
Gluten is
a substance found in wheat rye and barley. when a person with celiac disease eats such food. the immune system of the body reacts with gluten and try to destroy it but in this process the microvilli also destroy, and this results in malabsorption and symptoms like diarrhoea and weight loss.
Symptoms of celiac disease:
- abdominal bloating and pain
- chronic diarrhoea
- vomiting
- constipation
- pale, foul-smelling, or fatty stool
- weight loss
symptoms vary from person to person.
Irritability is another common symptom in children. Malabsorption of nutrients during the years when nutrition is critical to a child’s normal growth and development can result in other problems such as failure to thrive in infants, delayed growth and short stature, delayed puberty, and dental enamel defects of the permanent teeth.
Adults are less likely to have digestive symptoms and may instead have one or more of the following:
- idiopathic (of unknown cause) iron deficiency anaemia.
- fatigue
- bone or joint pain
- arthritis
- bone loss or osteoporosis
- depression or anxiety
- tingling numbness in the hands and feet
- seizures
- missed menstrual periods
- infertility or recurrent miscarriage
- canker sores inside the mouth
- an itchy skin rashes
Researchers are studying the reasons celiac disease affects people differently. The length of time a person was breastfed, the age a person started eating gluten-containing foods, and the amount of gluten-containing foods one eats are three factors thought to play a role in when and how celiac disease appears. Some studies have shown, for example, that the longer a person was breastfed, the later the symptoms of celiac disease appear.
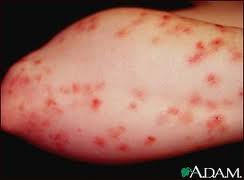 |
| dermatitis herpetiformis |
Symptoms also vary depending on a person’s age and the degree of damage to the small intestine. Many adults have the disease for a decade or more before they are diagnosed. The longer a person goes undiagnosed and untreated, the greater the chance of developing long-term complications.
Childhood Clinical Presentation:
ltypical
¡failure to thrive
¡diarrhea/steatorrhea
¡anorexia
¡vomiting
¡abdominal distension
¡abdominal pain
latypical
¡aphthous ulcers.
¡short stature
¡anemia
¡rickets
Adult Clinical Presentation
ltypical
¡ diarrhoea/steatorrhea (75-80%)
¡weight loss
¡abdominal bloating/flatulence
¡mild abdominal pain
latypical
¡anemia (85%)
¡osteoporosis (15-30%)
¡coagulopathy (10%)
¡aphthous ulcers
¡infertility/menstrual abnormalities
¡neurologic symptoms
¡short stature
¡weakness/myopathy
Diagnosis is made with the help of:
Blood Tests, skin rash (dermatitis herpetiformis) intestinal biopsy, screening.
Treatment:
The treatment for Celiac disease is a Gluten free diet. it means we have to avoid food containing wheat rye of barley.
Allowed foods
| amaranth arrowroot buckwheat cassava corn flax Indian ricegrass Job’s tears | legumes millet nuts potatoes quinoa rice sago | seeds sorghum soy tapioca teff wild rice yucca |
Avoid foods like;
wheat
| barley rye triticale (a cross between wheat and rye) | |
Important Points;
- People with celiac disease cannot tolerate gluten, a protein in wheat, rye, and barley.
- The untreated celiac disease damages the small intestine and interferes with nutrient absorption.
- Without treatment, people with celiac disease can develop complications such as osteoporosis, anaemia, and cancer.
- A person with celiac disease may or may not have symptoms.
- Diagnosis involves blood tests and, in most cases, a biopsy of the small intestine.
- Since celiac disease is hereditary, family members of a person with celiac disease may wish to be tested.
- Celiac disease is treated by eliminating all gluten from the diet. The gluten-free diet is a lifetime requirement.
- A dietitian can teach a person with celiac disease about food selection, label reading, and other strategies to help manage the disease.
Reference:
Robin's Basic Pathology
Robin's Basic Pathology
https://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pubs/celiac/#what
There is only one treatment, adopting a celiac disease diet which is essentially a gluten free diet- no medication exists at the moment. If a strict diet is followed the gut heals, and symptoms reduce. However it is not a cure all and the quality of life may well be lower for celiacs.
ReplyDeleteWhat is Celiac Disease