Local Cardiac examination:
Inspection and Palpation.Percussion.
Auscultation.
Inspection and Palpation
A- Shape of the precordium:-Precordial bulge®denotes cardiac enlargement since childhood.
-Skeletal deformities :
Such As kyphosis, scoliosis or pectus excavatum.
These may cause alteration of the position of the heart and great vessel which may predispose to heart failure.



Apex Beat:
Examine for :1-Visible or not. (causes of invisible apex ? )
2-Site: (Apex beat is the outermost and lowermost palpable impulse on the chest wall. )
* Normally in the left 5th intercostal space, just inside the Midclavicular line (MCL) (9 cm from the mid line ).
*Abnormalities in site :
-Outward displacement----®Right ventricular enlargement, chest disease.-Outward and downward ®Left ventricular enlargement, ventricular Aneurysm
-Displacement to Rt.-------®congenital Dextrocardia, chest disease
3-Extent :
Localized apex: Normal apical impulse do not exceed an inch in diameter ( Lt. V. apex )4- Character:
*Heaving sustained: ®Pressure overload ®causes: Aortic stenosis and hypertension.*Hyperdynamic apex: causes (Volume overload ®aortic regurgitation, Mitral Regurgitation, Tricuspid Regurgitation)
*Slapping apex ®Palpable S1 ®Mitral stenosis
5. Thrill
Murmurs may be so loud as to be palpable as thrill.It is a palpable vibration of the chest wall similar to feeling back of a purring cat.
-It should be timed with apex beat, either systolic or diastolic.
-Diastolic thrill ®M.S.
-Systolic thrill ® M. R.
-It is most easily felt when the patient turns on to the left side.

Percussion
Surface anatomy of heart
Surface markings of heart borders;
A = 1.5 inch from the midline on the

the lower border of 2nd left costal cartilage.
B =1 inch from the midline on the upper
border of the 3rd Rt. Costal cartilage.
C =3.5 inch from the midline in the
left 5th intercostal space.
D =0.5 inch from the midline on the
Right 6th costal cartilage.
How to percuss the heart?
-Percussion of the right border of the heart.-Percussion of the base of the heart.
-Percussion for dullness outside the apex.
-Percussion of the bare area of the heart
Percussion Of Heart:
1-Rt. Border:
First, percuss the upper border of the liver in the Right midclavicular line., then percuss one space above the upper border of the liver, from Right to Left., parallel to the sternum.
-Normally there is no dullness to the Right side of the sternum.
-Causes of dullness to the Rt. Of the sternum :
* Right Atrial Enlargement.
* Pericardial effusion.
*Aneurysm of the ascending aorta
2. Percussion of Base Of The Heart (Upper border)
Percuss the 2nd Right And Left Intercostal spaces from MCL (midclavicular line) to the sternum.Normally both are resonant.
Causes of dullness in the Left 2nd space :
-Dilated pulmonary artery as in, pulmonary hypertension, ventricular septal defect, ASD.
-Pericardial effusion.
-space-occupying lesions in the superior mediastinum.
Causes of dullness in the 2nd Right Intercostal Space:
-Dilatation of ascending aorta, a huge aneurysm in the aortic arch.
-pericardial. Effusion and space-occupying lesion in the superior mediastinum.
3. Percussion of Left border:
Normally there is no dullness outside the apex.Dullness outside apex = pericardial effusion .
Auscultation Of Heart:
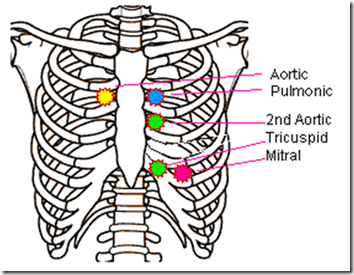
Auscultatory Areas :Mitral area
Pulmonary area.
First Aortic area.
Second Aortic area.
Tricuspid area
Comment on :
a- Heart sounds.b-Additional sounds.
c- Murmurs.
d- Pericardial rub. (Pericarditis)
a) Heart Sounds:
First heart sound ( S1 ) is produced as a result of the closure of the AV valve.-Best heard at Mitral area, at the beginning of systole
-Accentuated S1 is heard in case of mitral stenosis.
.
-Weak S1 is heard in case of
1. mitral regurgitation.
2. calcified mitral valve.
3. Severe heart failure
-Variable S1 Is heard in case of atrial fibrillation.
Second heart sound (S2 ):
Produced by Closure of aortic &pulmonary valves
Best heard at the base of the heart, at the beginning of diastole.
Abnormalities :
On pulmonary area :
-Accentuated in pulmonary hypertension
On Aortic area :
-Accentuated A2 in found in Hypertension and Hyper dynamic states
-Weak A2 is found in aortic stenosis
B-Additional heart sounds
1-Gallop rhythm
It is hearing of 3 sounds (1st, 2nd, and extra sound ) in the presence of tachycardia(like a galloping horse)
2. Murmurs:
Murmurs are produced by excessive turbulence of blood flow within the circulation.A- Systolic murmurs
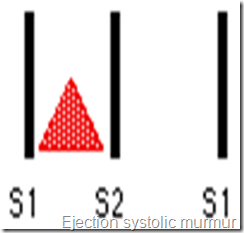
1-Ejection systolic murmur
-It begins shortly after S1 and ends before S2.
--Result from turbulent blood flow through sensed semilunar valves or blood flow through the normal valve.
-Examples: Aortic stenosis ( Aortic area )
-Pulmonary stenosis, ASD. (pulmonary area )
2-Pansystolic murmur
Begin with S1
Extend throughout systol &
may spill over into early diastole
Examples: MR, VSD.

B: Diastolic Murmur:
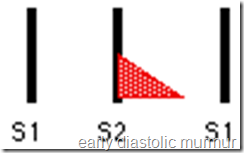
1-Early diastolic murmur
-It starts immediately after S2
-Soft blowing.
-loudest at its onset and dies away before the end of diastole(Decrescendo)
-Best heard when the patient leans forward and expiration.
-The result from leaking semilunar valves.
Causes: Aortic regurgitation and heard best at Second aortic area.
Pericardial Rub:
Scratching sound like friction between rough surfaces and has superficial to and fro quality.
Best heard to the left of the lower sternum
It is accentuated when the patient leans forward and by pressure with a stethoscope.
(Y)
ReplyDelete