Causes Of Pulmonary Embolism
1. Emboli:
Thrombi in deep veins of legs are the usual source of pulmonary emboli
2. Thrombi
Pulmonary hypertension, pulmonary atherosclerosis and heart failure are common causes of formation of pulmonary Thrombi (although it is rarer than emboli)
Morphology:
1. Large emboli occlude larger arteries leading sudden enlargement of the right ventricle (cor pulmonale) leading to syncope or sudden death.
2. In the normal circulatory system when small emboli block the smaller pulmonary arteries, it will not result in infarction, because normal bronchial arterial supply fulfils the requirement of the lung parenchyma, in this case only Pulmonary haemorrhage will be there.
Bronchial arteries arise from aorta and supply lungs. therefore, lungs have a dual blood supply, one comes from the left ventricle through bronchial arteries and the other comes from the right ventricle through pulmonary arteries.
3. In the case of the abnormal circulatory system (that is heart or lung disease), small emboli cause infarction.
4. Lower lobes are mostly affected
5. On chest X-ray, the infarcted zone is wedge-shaped with its base at the periphery of lung and apex pointing towards the hilum.
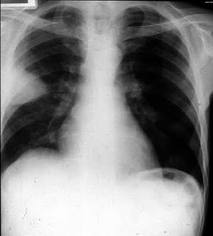 |
| Chest X-ray showing wedge-shaped Pulmonary infarction on the right side. |
1. Respiratory Compromise. Breathing will be difficult, and the patient experiences shortness of breath
2. Hemodynamic compromise: Blood pressure will decrease.
In Case Of Small Emboli:
1. dyspnea (shortness of breath)
2. Tachypnea (Respiratory rate increases)
3. Fever
4. Chest pain
5. Cough
8. Hemoptysis
In Case Of Large Emboli.
9. Syncope or sudden death.